The spectrum and colors of light.
Light is a stream of photons emitted by a source such as; the sun, a bulb or an LED chip.
14 November 2023
Regardless of the source, photons are always of the same nature. We characterize them by their wavelength, which is directly related to their energy. By property, the shorter the wavelength, the more energy it carries. Light wavelengths (λ) have the unit nanometre (nm) as their unit. It is by this unit that we can classify any type of radiation. In this classification we find ultraviolet light (UV) from 200 to 400 nm, blue light from 400 to 500 nm, green light from 500 to 600 nm, red light from 600 to 700 nm, near infrared light (NIR) from 700 to 800 nm and finally infrared light (IR) from 800 to 1,200 nm.
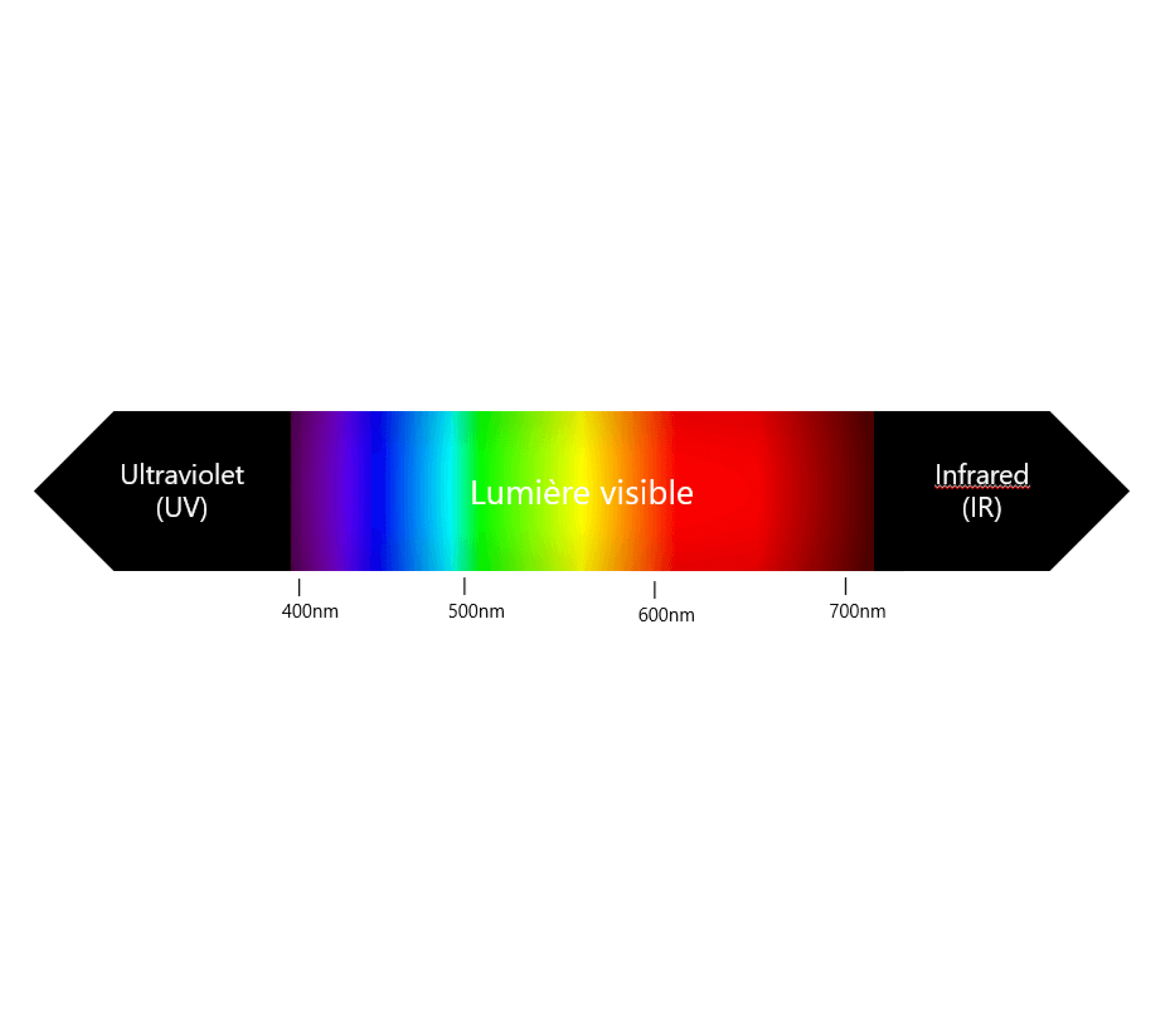
Figure 1 : Electromagnetic spectrum following wavelength.
Any light source emits radiation. Monochromatic radiation is a beam with only one wavelength. This is the case with lasers and certain LEDs known as monochromatic. Polychromatic radiation is radiation that contains several wavelengths. This is the case with the sun, white LEDs, HPS and other sources. The set of wavelengths and their respective intensities making up radiation is called the emission spectrum.
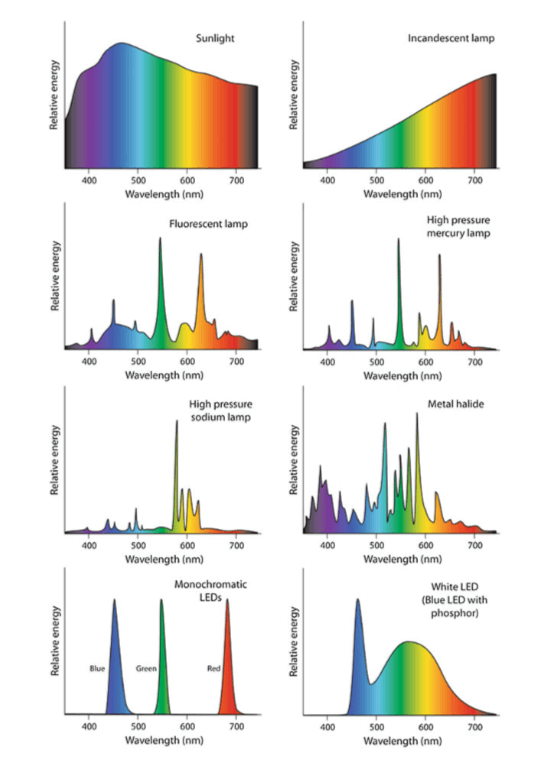
Figure 2 : Spectrum of different light sources (Dutta Gupta et Agarwal. 2017).
Emission spectra vary according to the light sources used in horticulture as shown on the following images:


